關於我們About us
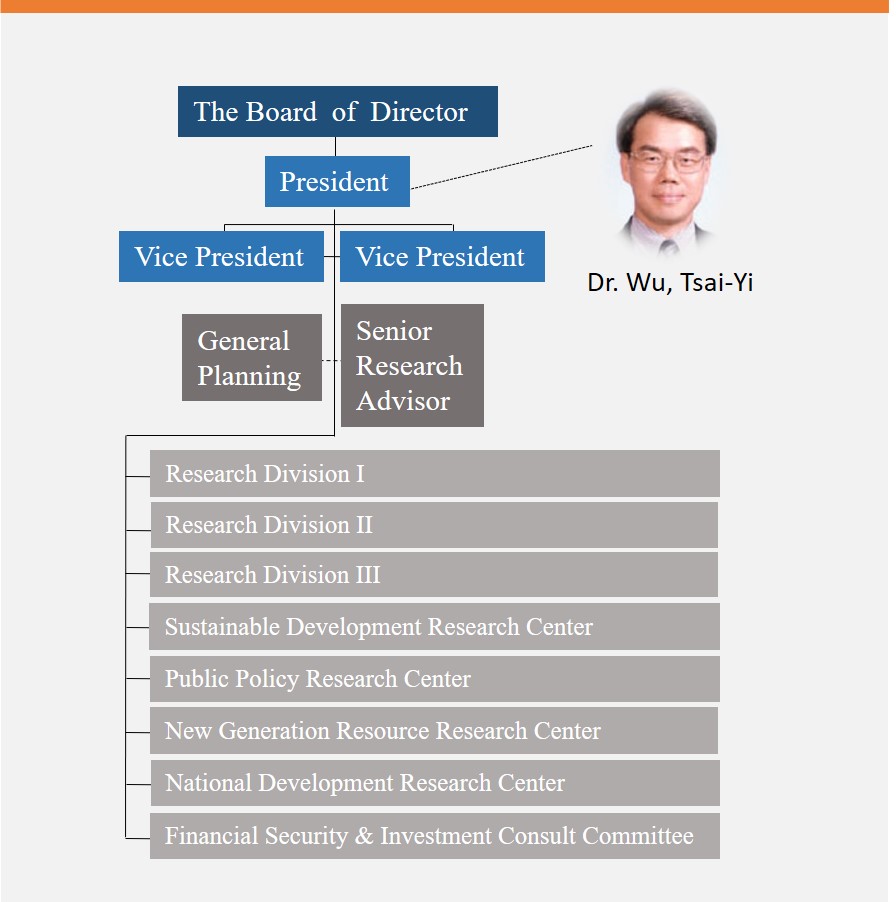
Taiwan Research Institute (TRI) was established in 1994 as a privately funded non-profit organization and a non-partisan specialized think tank. TRI consists of 3 research divisions, 4 research centers and 1 consult committee with 33 staffs, 158 research fellows and 191 employees. TRI’s research topics mainly focus on energy policy, electricity management, environmental policy, renewable energy development and greenhouse gases emissions reduction policy. TRI is expertise in policy and planning, knowledge management, and impact assessment.
As climate change and sustainability and its environmental, social and economic impact continue to rise on the agendas of governments and organizations around the world, TRI started to provide the government of Taiwan with consultancy services on sustainable development at a very early stage. Research Division III provides quantitative and qualitative analyses mainly in three research fields including climate change and sustainable development, green finance and 3E models. Our efforts in these topics are described in more detail in the following sections
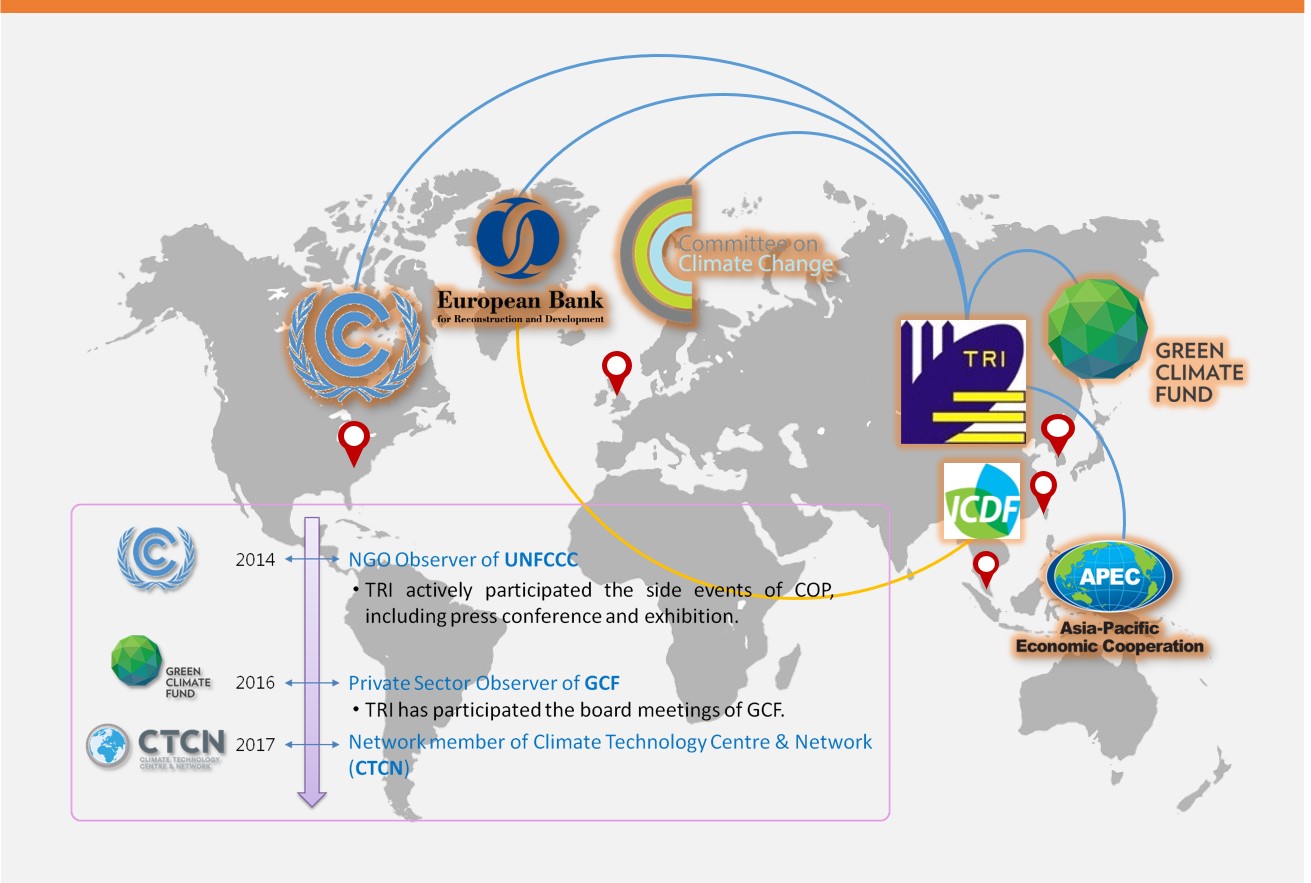
To keep our analytical tools in accordance with global methodologies, TRI is not only highly engaged in the policy decision making process in Taiwan but also participate in international climate change meetings actively.
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is one of the most dominant international environmental treaty in the world with 197 signatory nations. Hence TRI takes part in the network of UNFCCC, including Green Climate Fund (GCF) and Climate Technology Centre & Network (CTCN), both the finance and technology mechanisms of UNFCCC as an observer NGO. We attend the Conferences of the Parties (COP) and the board meetings of GCF every year, exchanging information and seeking cooperation with other organizations through arranging the exhibit booth and side events.
TRI’s plays an important role in the formulation and implementation of GHG management policies in Taiwan.
The impacts of climate change are becoming more frequent and severe. At the 21st Conference of the Parties (COP21) in December 2015, Paris Agreement was adopted as the first-ever universal, legally binding global climate deal which has set out global emission reduction targets and established a set of binding procedural commitments of the nationally determined contributions of the parties. The Agreement soon entered into force on 4 November 2016.
In response to the global trends, Taiwan has been pursuing policies to cut the greenhouse gas emissions for many years. The “Greenhouse Gas Reduction and Management Act” (the Act) were enacted in 2015. To provide financial support to the efforts in combating climate change of both mitigating greenhouse gas emission and adapting impact of climate change, article 19 of the Act authorize the establishment of the Greenhouse Gas Management Fund.
TRI helps the Environmental Protection Administration (EPA) to complete the legal and operational frameworks of Greenhouse Gas Management Fund and to develop proper financial tools to promote climate mitigation and adaptation activities and mobilize private capital in accordance with the ultimate goal of mainstreaming climate and green finance.
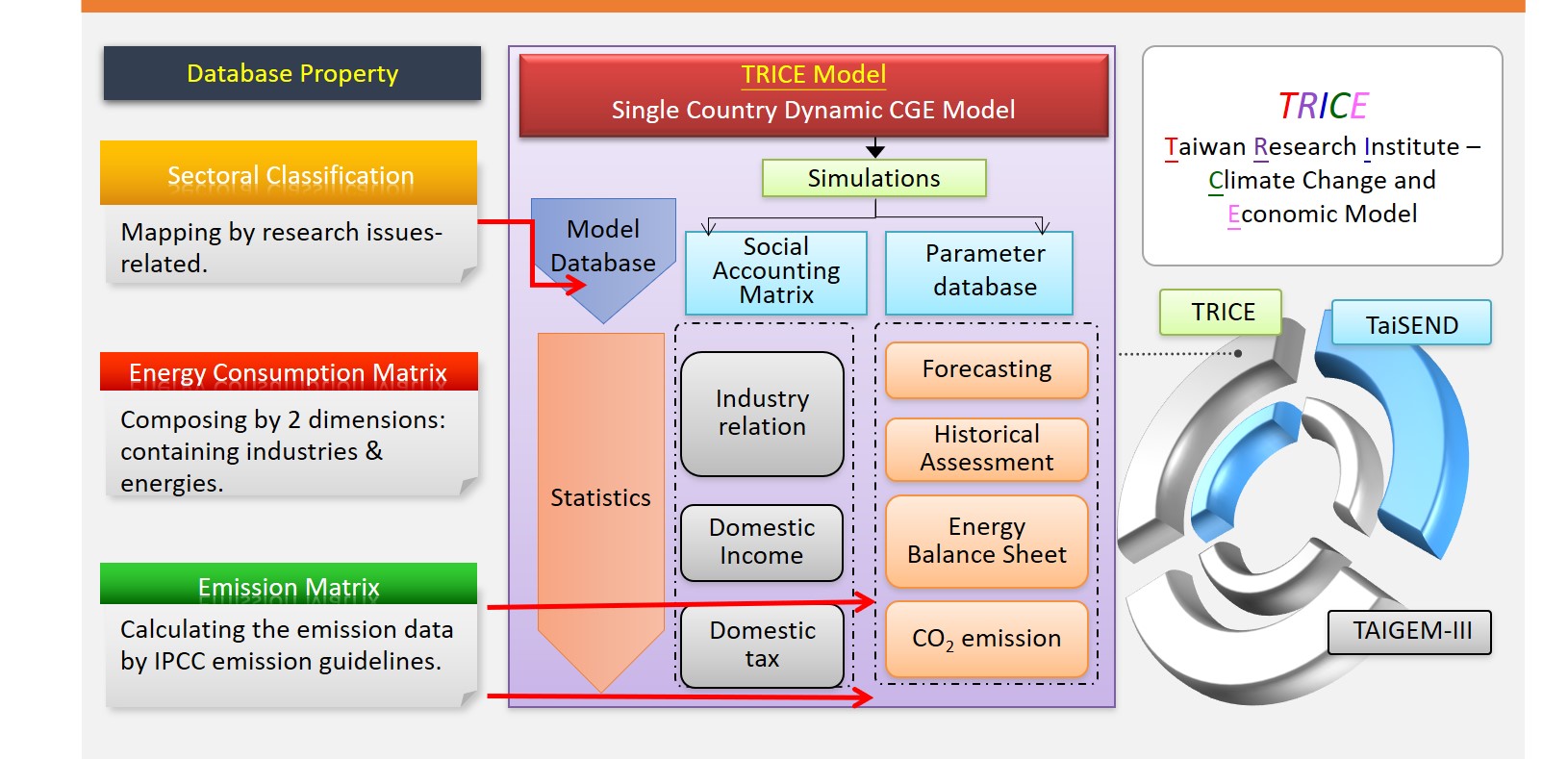
The twin challenges of energy security and climate change have driven an intense modelling activity of long term energy-economy-environment (3E) scenarios over the past decade. As a global consensus on the reality of climate change and on the urgency to act becomes an irreversible trend, policy makers rely heavily on the advice on a balanced path of economic growth.
Besides, early development of energy and environment statistics made it possible to develop computable multisectoral general equilibrium models (CGE-models) with a rigorous description of energy supply and demand, and the interlinkages between economic activity, energy production and use, and emissions to air. These integrated CGE-models have been used for forecasting purposes and numerous analyses of energy and environmental policies during the last two decades. Especially the models have been developed to be suitable for analyzing different economic policy options to deal with the global climate issue as design of optimal carbon tax or carbon quota schemes.
In order to provide policy makers in Taiwan with mathematical insights on mapping out the path of sustainable economic growth, TRI has developed and maintained the CGE models, including TAIGEM, TaiSEND, and TRICE for evaluation of 3E’s related policies.